Lake Qinghai, China
Reference
Liu, Z., Henderson, A.C.G. and Huang, Y. 2006. Alkenone-based reconstruction of late-Holocene surface temperature and salinity changes in Lake Qinghai, China. Geophysical Research Letters 33: 10.1029/2006GL026151.
Reference
Liu, Z., Henderson, A.C.G. and Huang, Y. 2006. Alkenone-based reconstruction of late-Holocene surface temperature and salinity changes in Lake Qinghai, China. Geophysical Research Letters 33: 10.1029/2006GL026151.
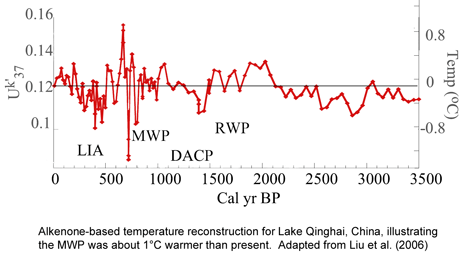
Description
The authors developed a quantitative reconstruction of temperature changes over the past 3500 years based on alkenone distribution patterns in a sediment core retrieved from China's Lake Qinghai (37°N, 100°E), based on the alkenone unsaturation index that has been calibrated to the growth temperature of marine alkenone producers and "to temperature changes in lacustrine settings on a regional scale." This work revealed that the peak warmth of the Medieval Warm Period (AD 900-1500) exceeded the temperature of the latter part of the 20th century by about 0.5°C.