Reference
Richey, J.N., Poore, R.Z., Flower, B.P. and Quinn, T.M. 2007. 1400 yr multiproxy record of climate variability from the northern Gulf of Mexico. Geology 35: 423-426.
Description
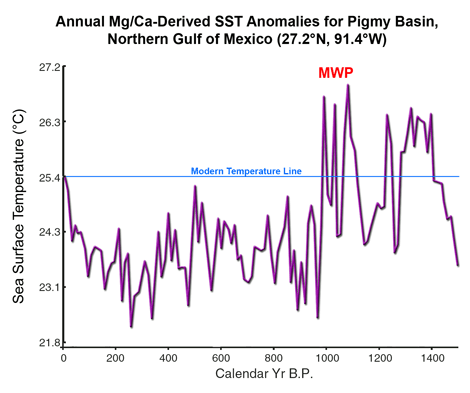
In the words of the authors, "a continuous decadal-scale resolution record of climate variability over the past 1400 years in the northern Gulf of Mexico was constructed from a box core recovered in the Pigmy Basin, northern Gulf of Mexico [27°11.61'N, 91°24.54'W]," based on climate proxies derived from "paired analyses of Mg/Ca and δ18O in the white variety of the planktic foraminifer Globigerinoides ruber and relative abundance variations of G. sacculifer in the foraminifer assemblages." This work revealed that "two multi-decadal intervals of sustained high Mg/Ca indicate that Gulf of Mexico sea surface temperatures were as warm or warmer than [italics added] near-modern conditions between 1000 and 1400 yr B.P." From the author's Figure 1 (adapted below), we calculate the peak warmth during this time to have been about 1.5°C warmer than present-day temperatures.