Lake Teletskoye, Altai Mountains of Southern Siberia, Russia
Reference
Andreev, A.A., Pierau, R., Kalugin, I.A., Daryin, A.V., Smolyaninova, L.G. and Diekmann, B. 2007. Environmental changes in the northern Altai during the last millennium documented in Lake Teletskoye pollen record. Quaternary Research 67: 394-399.
Reference
Andreev, A.A., Pierau, R., Kalugin, I.A., Daryin, A.V., Smolyaninova, L.G. and Diekmann, B. 2007. Environmental changes in the northern Altai during the last millennium documented in Lake Teletskoye pollen record. Quaternary Research 67: 394-399.
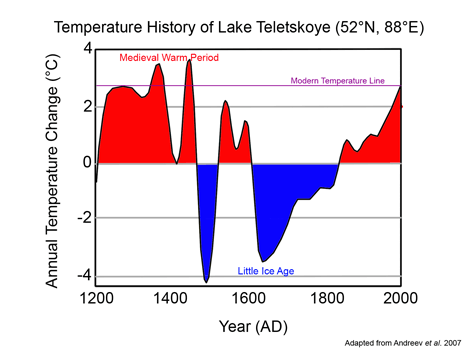
Description
Working with a sediment core extracted from the central and deepest part of Lake Teletskoye in the northeastern part of the Altai Mountains in southern Siberia (51°43'N, 87°39'E), the authors analyzed pollen and charcoal stratigraphy to develop "the first detailed climate and vegetation reconstruction for the last millennium in the northern Altai Mountains." This work revealed the existence of a period "at least since ca. AD 1020" when "climate conditions were similar to modern [our italics]." Then, "around AD 1200, climate became more humid with the temperatures probably higher than today [our italics]," and this period "lasted until AD 1410."